class g airspace visibility requirements
Above 10000ft MSL the requirements are 5 SM visibility and cloud clearance of 1000ft above 1000ft below and 1 SM horizontally. A Unless otherwise specified in the certificate holders operations specifications when conducting VFR helicopter air ambulance operations in Class G airspace the weather minimums in the following table apply.
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums Bobbie Lind
A Unless otherwise specified in the certificate holders operations specifications when conducting VFR helicopter air ambulance operations in Class G airspace the weather minimums in the following table apply.

. 36 rows Notwithstanding the provisions of paragraph a of this section the following operations may be conducted in Class G airspace below 1200 feet above the surface. The basic VFR weather minimums for operating an aircraft within class D airspace are VFR flight in controlled airspace above 1200 feet AGL and below 10000 feet MSL requires a minimum visibility and vertical cloud clearance of 3 miles and 500 feet below or. 3 statute miles 500 below 1000 above 2000 horizontal.
VFR Minimum Distance from Clouds Below 10000 MSL. Cloud clearances range from clear of clouds to 1SM There are 6 sets of Class G weather minimums associated with various altitudes during the day or night. For Class B C D and E airspace below an altitude of 10000 MSL the basic VFR weather minimums are.
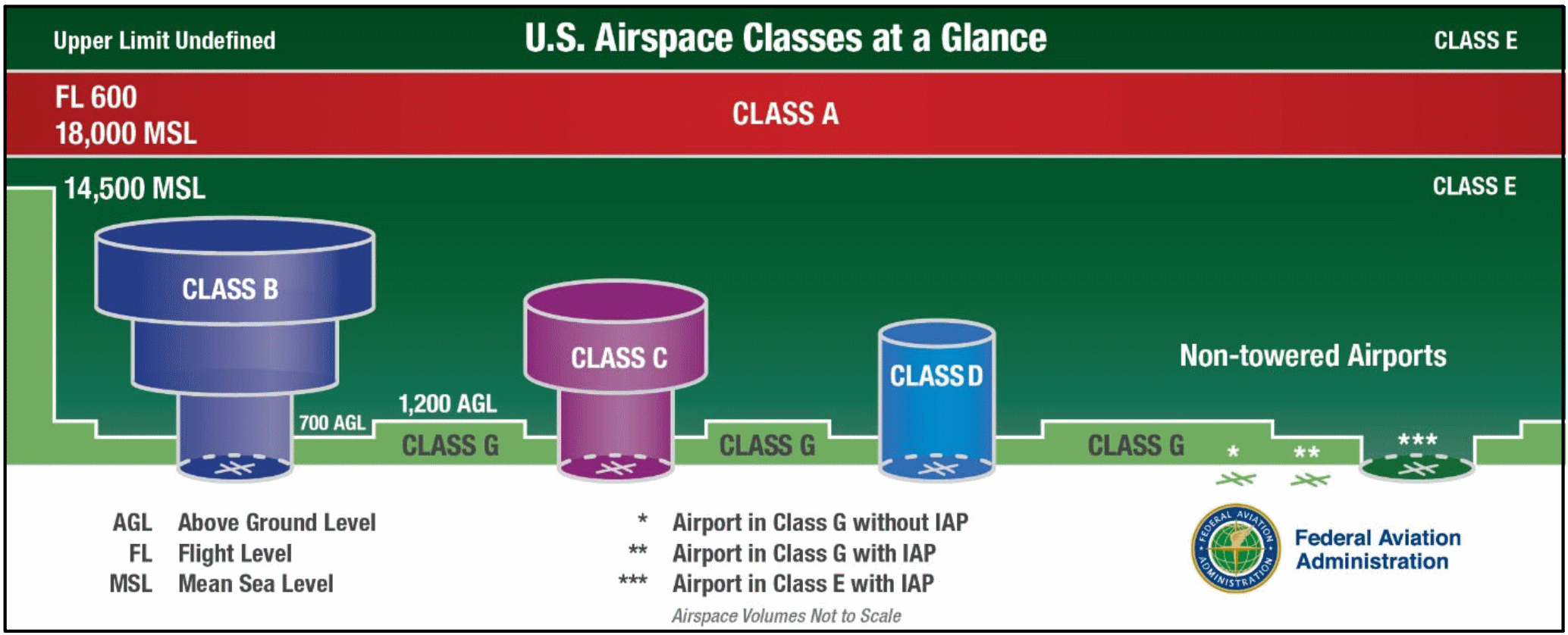
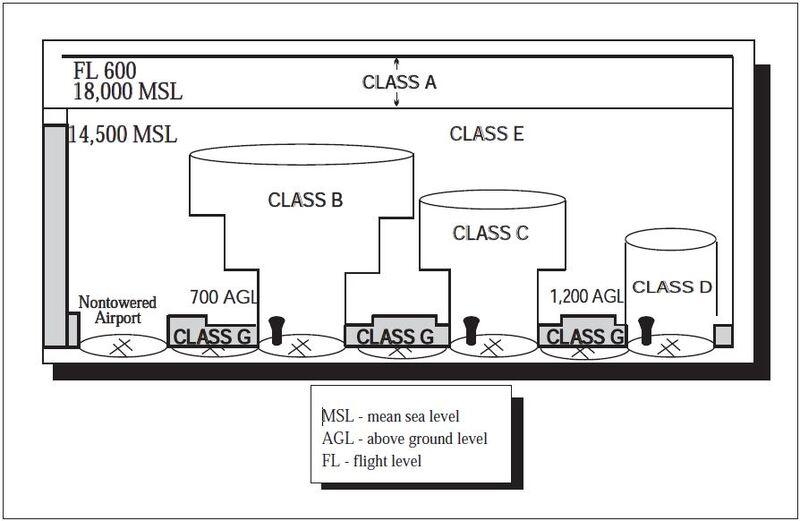
Flight visibility of 3 statute miles SM Cloud clearance of 1000 above 500 below and 2000 horizontally except for class B which simply requires pilots to remain clear of the clouds. Rules governing VFR flight have been adopted to assist the pilot in meeting the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft. Class G airspace uncontrolled is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as Class A Class B Class C Class D or Class E airspace.
Minimum flight visibility and distance from clouds required for VFR flight are contained in 14. Two-way communication with ATC must be established before entering class D airspace but no transponder is requiredVFR cloud clearance and visibility requirements are the same as class C. Class G airspace is usually found below 1200 feet where Class E airspace typically starts although there are of course exceptions.
During the day less than 1200 AGL in class G airspace the flight visibility requirements are ½ statue mile and the cloud clearance requirements are to remain clear of clouds. August 16 2018 by ETL. 1200 feet or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude For aircraft other than helicopters.
B A certificate holder may designate local flying areas. Class G Is The Most Lenient And Confusing. 3 statute miles 500 below 1000 above 2000 horizontal.
Class G airspace is more prevalent and may be found at lower altitudes in less dense areas of the country where IFR operations are less common. 135609 VFR ceiling and visibility requirements for Class G airspace. Class D airspace reverts to class E or G during hours when the tower is closed or under other special conditions.
Click to see full answer Likewise people ask what minimum visibility and clearance from clouds are required for VFR. Day - 1 Statute Mile Night - 3 Statute Miles. Depending on how high you fly and the time of day within Class G airspace your visibility requirement could range anywhere from 1SM to 5SM.
At night requirements jump to three miles visibility and from merely clear of clouds to 500 feet below 2000 feet horizontal and. 500 Below 1000 Above 2000 Horizontal. At night less than 1200 AGL in Class G airspace the helicopter flight visibility requirements are 1 statue mile visibility and cloud clearance.
Day except as provided in 91155 b 1 statute mile. What are the ATC requirements for Class A airspace. 12 rows 1200 feet or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude 1 statute mile.
At night in Class G between 1200 AGL and 10000ft MSL the visibility and cloud clearance are the same as Class CD. Click to see full answer Similarly is a transponder required in Class D airspace. On the other hand Class G airspace has four different sets of altitude-dependent minimums.
One mile visibility and clear of clouds is the daytime requirement. 500 Below 1000 Above 2000 Horizontal 500 Below 1000 Above. June 4 2021.
VFR Minimum Visibility Below 10000 MSL. 500 Below 1000 Above 2000 Horizontal. You can remember Class G uncontrolled airspace because its just like the good old days at the dawn of aviation.
For aircraft other. 135609 VFR ceiling and visibility requirements for Class G airspace. A helicopter may be operated clear of clouds in an airport traffic pattern within 12 mile of the runway or helipad of intended landing if the flight visibility is not less than 12 statute mile.
Class G 1200 feet or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude. Night except as provided in 91155 b 3 statute miles. Related Article Class G Airspace Explained.
G night 3 statute miles 152 4500 below 41000 above 42000 horizontal G day 1 statute mile. All operations in Class A Class B Class C and Class D airspace or Class E airspace designated for an airport must receive prior ATC authorization as required in 10317 of this part.

Airspace Classes And Special Use Airspace Everything There Is To Know

Sectional Airspace Summary Aviation Education Aviation Classes Aviation

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

Vfr Cloud Clearances Pilot Training For Ga
What Are The Basic Vfr Minimums Quora

4 Airspace Guidelines Scanifly

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

Uncontrolled And Controlled Airspace

What Are The Different Airspace Classes Flying Magazine

Faa Airspace For Vfr Flight Youtube

Activities Courses Seminars Webinars Alc Content Faa Faasteam Faasafety Gov